How to Apply Topical Solutions for Effective Headache Relief

Headaches

Headaches…Types & Treament
Headaches are one of the most common ailments affecting thousands of people every day. Migraine headache alone directly affects about 12% of the population and the cause of a migraine headache is still a mystery to the medical profession. The symptoms and pain associated with the various types of headache, including cluster headaches, can be difficult for your doctor to pinpoint. This makes it hard to pinpoint exactly what type of headache is the problem and the best course of action for headache relief.
We encourage all headache sufferers to consult their doctor if they are unsure of what type of headache they suffer from or if they have any questions regarding treatment particularly in the case of cluster headaches.
Almost everyone gets headaches, but not all headaches are the same. Some are a mild in nature while others are so severe you cannot function.
There are different types of headache, everything from tension headache, cluster headaches, to migrain headaches… each is bought on by different causes for the headache and therefore require different heatreatments for the specific type of headache.
A frequent headache is rarely the symptom of a severe disorder, such as a brain tumor. However, it does mean something is wrong, so it should not be ignored. It’s particularly important to seek medical help if your headaches are severe or keep coming back. Repeated episodes and increase in headache severity are the key indicators of something more severe such as a migrane headache or cluster headaches.
You don’t have to just ‘live with’ headaches. Effective headache relief is available for all types of headaches, even migraine, and there are effective cluster headache remedies. By recording when and how your headaches occur, you can help your doctor diagnose and find the right treatment for your headache.

Tension Type Headaches
Tension type headache is the commonest form of headache with up to two thirds of people experiencing it at some stage in their lives. To determine if a tension headache is the root cause for your headache
Tension Headache Symptoms
Tension headaches are usually felt on both sides of the head. The pain is dull and persistent, varying in intensity. A tension headache is often described as a feeling of pressure, heaviness or tightness in a band around your head.
Tension Headache Frequency & Duration
Episodic tension type headaches can last from 30 minutes up to a week. They usually occur infrequently, but can progress to what is known as a chronic headache condition, where frequent headaches occur all the time, with sufferers enduring headaches of varying intensity all day, every day, and they wake you up at night.
Generally, tension type headaches are diagnosed as being chronic when they are present for more than 15 days per month. In this case, a sufferer will notice the headache at the start of the day, and it will remain as a dull ache throughout the course of the day.
Possible Causes for a Tension Headache
Tension type headaches may be triggered by emotional or physical stress (eg. an argument, fatigue, prolonged reading, dehydration or sitting for a long time with bad posture), or by environmental factors such as loud music.
Treatment for a Tension Headache
• Lifestyle…Combat stress by keeping fit, getting regular sleep and exercise and eating a balanced diet. Some people find that learning specific relaxation techniques or posture improvement techniques such as yoga or meditation are effective because they tech you to relax your mind and your body, particularly during time of stress.
• Medication…Episodic tension type headaches are best treated with mild, over- the -counter analgesics such as aspirin (Aspro, Disprin), paracetamol (Panadol, Panamax, Dymadon). If the headache continues, you should take a shower or bath, apply a warm compress to your forehead and get some sleep.
• If your headaches occur daily and are diagnosed as being chronic tension type headache, your doctor may prescribe tricyclic antidepressants which have been shown to be useful in this condition and which may also be useful for any associated depression.
Some migraine sufferers (about 10%) also sufferer from tension headaches. It is important to keep an accurate record of the exact symptoms and triggers for all your headaches so that your doctor can see if you fall into this category and treat your headache accordingly. See you doctor if…
• your headache lasts more than 24 hours or occur more than three times a week.
• you headache wakes you up, or they are worse in the mornings
• your headache starts when you exercise, strain or cough
• your headache gets progressively worse over several days.

Sinus Headaches
Symptoms
A sinus headache usually occurs as a gnawing pain over or under both eyes. It usually accompanies blocked sinuses caused by bad cold, flu or allergies and can be associated with a rise in temperature. The affected area may be painful when touched. The headache gets worse as the day goes on and increases in intensity if you bend forward.
Sinus Headache Frequency
Sinus headaches can occur at any time, generally when a change of seasons or weather occurs.
Possible Sinus Headache Causes
Sinuses are air-filled spaces in the facial bones around the nose, which are part of your respiratory system. Sinus headaches are one symptom of sinusitis, where your sinuses become infected and inflamed.
Sinus Headache Treatment
• Lifestyle…If possible stay indoors in a room with an even temperature, as a dry overheated environment could make your high temperature and nasal congestion symptoms worse. Steam inhalation may be useful to try and clear the sinuses to reduce or avoid a sinus headache.
• Medication…Take aspirin or paracetamol to relieve your sinus headache. If your headache symptoms persist, you may need to see your doctor to be prescribed a broad spectrum antibiotic to combat the sinus infection and possibly a nasal decongestant to unclog your nose. If your sinusitis does not clear up, you may need to undergo a minor operation to remove any obstruction from your sinuses.
See your doctor if – Your sinus headache symptoms last for more than a couple of days.

Migraine (Vascular) Headache
A migraine headache affects one in eight adults in the developed world. People of any age can suffer, although adults aged 25-34 are most commonly affected, and women two or three times as frequently as men.
Migraine Headache Symptoms
The main migraine headache symptom is a moderate to severe throbbing pain, usually on just one side of the head. This is often accompanied by nausea (feeling sick), cold hands, vomiting and sensitivity to light and sound. The cause for migraine headaches is not known.
A migraine where people suffer an ‘aura’ or warning, 10 to 30 minutes before the migraine headache begins, only occurs in one in five headache cases. The aura may take many forms: lines or spots before the eyes, total darkness, tingling or numbness in the limbs and speech impairment. This can be a frightening experience.
Eighty percent of migrain headaches have no aura, although a few days beforehand you may feel irritable, lethargic and experience food cravings.
Migraine Headache Frequency & Duration
A migraine headache attack occurs on average once a month and usually lasts between 4 and 72 hours.
Possible Cause for Migraine Headaches
There is a wide range of possible triggers associated with a migraine headache.
They include:
• bright or flashing lights irregular sleeping or eating patterns
• loud noises and strong smells sudden weather or altitude changes
• emotional factors, such as stress, fatigue or excitement.
Women may find fluctuating hormone levels (due to ovulation, menstruation, or birth control pills) are a contributing factor to the cause for migraine headaches.
Your diet can also make you vulnerable to migraine headache: red wine, cheese, chocolate, nuts, soy sauce, citrus fruit, alcohol, excess caffeine (eg. cola, tea, coffee) and some food additives (monosodium, glutamate, sodium nitrate) are all possible migrain headaches triggers.
Treatment for Migraine Headaches
• Lifestyle…One way to manage headaches is to learn to recognise if there are ‘triggers’, so they can be avoided. Keeping a diary will help by highlighting suspect events, moods or foods. Given that stress is one of the most common triggers for migraines, relaxation such as yoga or meditation may be helpful.
However, only a minority of people with migraine can clearly identify what triggers their attacks and even if triggers can be identified, they can not always be avoided. We have provided Links to Support Organizations that will provide further information about lifestyle changes you can make to help manage a migraine headache.
• Medication…Until recently, doctors were relatively limited in managing migraine headaches. However, modern medicines are now available that can help minimize the disruption migraine headaches can make to your everday life.
• Mild migraine headache pain can be treated with analgesics (eg. aspirin, paracetamol), antihistamines and anti-emetics (to combat nausea).
• Severe migraine headache pain can be treated with Menastil, and CorProfen which are available on this web site.
If you suffer two or more migraine headaches a month, your doctor may prescribe preventative medication., which is used when migraines are severe or frequent enough to disrupt your life. This continuous, daily medication should help you to reduce the number of migraine headaches and may eliminate them altogether.
For moderate or severe attacks which are not too frequent, you may prefer effective, on the spot acute treatment for your migraine headache rather than daily preventatives. In this case, medications such as sumatriptan (Imigran) or ergotamine can effectively reduce the severity and the duration of migraine pain and its associated symptoms.
See your doctor if – You think you might be suffering migraine headaches or if you are not satisfied with your current migraine headache treatment. If you have been suffering from migraines for years, the cause for a migraine headache is still not known but there are now more effective headache relief treatments are available.

Migraine (Vascular) Headache
Temporal arteritis is not common, and often affects people over the age of 55.
Symptoms
Head pain is described as persistent, waxing and waning throughout the day, and may occur anywhere on the head, although it is often over the temples. It may be severe, burning and throbbing in the early course of the disease and non-throbbing later. Other symptoms are eyesight problems, mild fever, weight loss and jaw pain when chewing.
Frequency & Duration
Once diagnosed long term management can prevent recurrences.
Possible Causes
Temporal arteritis is caused by inflammation of the arteries which supply your head with blood.
Treatment Medication
If your symptoms are suggestive your doctor will perform a blood test and possibly a biopsy (the removal of a small piece of tissue under local anaesthetic for testing). Prompt and appropriate anti-inflammatory medication is essential to reduce the inflammation of the affected arteries and protect eyesight.
See your doctor if – You have these symptoms, or if you are over 50 years of age and develop a new, persistent headache as serious complications may develop and these can be avoided by prompt treatment.

Cluster Headaches
Cluster headaches are rare, severe and mainly affect men.
Symptoms
Severe headache pain developing around or behind one eye, which usually occurs at nights and wakes the sufferer from sleep. Congestion of the eye and nose on the affected side produces tears and nasal blockage and discharge on that side.
Frequency & Duration of cluster headaches
Cluster Headaches usually last between 15 and 90 minutes and can occur almost daily in groups or “clusters” for days or weeks at a time. Then they may disappear for a year or more.
Possible Cluster Headaches Causes:
There is some evidence that excessive smoking and /or alcohol consumption can trigger cluster headaches.
Cluster Headache Remedies
Medication…The migraine medication sumatriptan (Imigran) has proven effective in injection form for treating cluster headache. Pure oxygen inhalation is also used to alleviate an attack.
See your doctor if – You think you suffer from cluster headaches.

Headaches in General
This Web Site cannot be completely comprehensive when it come to headaches and headache cause and is intended as a guide only. Our information may change in the future. Visit the relevant website links we have provide for updates. If you have further questions you should raise them with your own doctor.
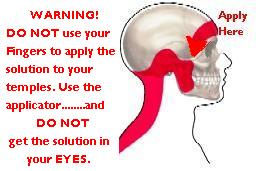
Menastil and/or CorProfen– Apply to your temples as indicated above for headache relief… Apply a very slight amount of either of these topical solutions to a spot about the size of a quarter to each temple, let it dry and wait 5 – 10 minutes and if no headache relief, apply once more. If no relief, the source of your headache is due to pain occurring at some other place on your body. See the other conditions on this site to pinpoint those areas as the source of your headache. Once pinpointed, Menastil and CorProfen can be equally effective in these locations as effective as when applied to your temples.
WARNING: DO NOT APPLY WITH YOUR FINGERS, USE THE APPLICATOR ON THE BOTTLE. DO NOT GET EITHER OF THESE PRODUCTS IN YOUR EYE’S. IF YOU DO, WASH OUT WITH WATER AND WAIT 15 MINUTES FOR THE BLUR TO GO AWAY.
REMEMBER: the cause for migraine headaches and cluster headaches is not known. The body of evidence suggests a myriad of reasons for each condition. Menastil is the most effective product among topical cluster headache remedies on the market today. CorProfen is also effective for migraine headaches and while not a cure, is a most effective headache management solution.